|
| Symptoms of a Meniscus InjuryWhat Does A Torn Meniscus Feel Like? Knee Pain Worsens With UsePain will become worse when you try to bend, straighten or twist your knee, during or after exercise (especially activities involving deep knee bends) and sometimes even just by putting weight on your knee. Your doctor may recommend that you use a crutch or cane to minimize the load placed on your torn meniscus to alleviate pain and further damage while you are trying to heal. Knee Stiffness and WeaknessYou may find that your range of motion is limited and that you are not able to bend or straighten your knee all the way. You may also experience a buckling or weakness in your knee that happens when a torn meniscus fragment slips out of being lodged between your bones. A reflex relaxation of the thigh muscles creates weakness in your knee joint resulting in poor stability. Degeneration of the Joint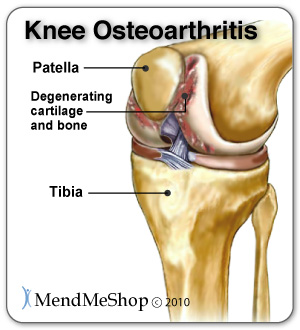 Degeneration is a very significant cause of lateral meniscus tears; over time, the edges of the meniscus become frayed, jagged, and thin. Any repetitive or frequent movement can place stress on the lateral meniscus over the years when evenually, all of a sudden, a meniscus tear happens. The knee joint itself suffers degenerative changes such as arthritis, osteoarthritis and/or cartilage thinning on the ends of the bones and this gradual wear and tear comes from overuse, repetitive knee movements, twisting or prolonged weight bearing activities. Degenerative changes to the knee happen slowly, so you may eventually suffer a torn lateral meniscus from a simple daily activity - the "hair that broke the camels back" if you will. Be aware that this injury can happen to anyone and is not just isolated to athletes.  Once injured, the meniscus is more susceptible to slowly wearing away with regular knee movements. When this happens more friction occurs against the articular cartilage and this cartilage wears away from the surface of the femur and tibia. With less protective covering, the joint begins to deteriorate. If your knee tissue begins to degenerate you have an increased risk of developing osteoarthritis (degenerative arthritis) over time. SwellingYou will experience swelling either immediately if your blood vessels are disrupted because of a traumatic event, or within 12 hours after the tear occurs. Swelling over time or recurring is a result of synovial fluid filling the joint cavity, as your body tries to protect itself (this is often called "water on the knee"). Grinding, Popping, Clicking, or LockingThese symptoms can range from being annoying to downright painful and can last a few seconds or be persistent for a few weeks. Joint locking occurs when the fragment of torn meniscus does not work its way out of being lodged between your femur and tibia resulting in an inability to straighten or bend your knee. This can be painful and may cause weakness in the knee or in some instances a 'giving way' or snaps, clicks, catches and/or jerks in the knee. You may have to manually move or manipulate your knee to get relief. Torn Meniscus StagesThere tend to be 4 stages of symptoms dependent on the type of meniscus injury you experience. Stage 1: Minor TearIf you have a minor tear you will often experience pain and slight swelling within the first 12 hours of noticing the discomfort. These symptoms often go away within a 2 - 3 week period. Stage 2: Moderate TearIf you have a moderate tear you will often have pain near the location of your meniscus tear, especially when twisting or squatting. Swelling will generally increase over 2 - 3 days, as will your stiffness, which will result in a limited range of motion when bending your knee. Symptoms will eventually go away but will tend to recur with minor twisting or overuse. Stage 3: Severe TearIf you have a severe tear, pieces of torn meniscus can move into your joint space and lead to a locked knee that is very swollen, stiff and painful. These symptoms come on quite quickly. Bruising and swelling with severe pain within minutes of an injury, generally indicate a tear of your ligament as well as your meniscus. Stage 4: Degenerative TearIf you suffer from a degenerative tear, it may not have resulted from one specific incident, but rather wear and tear over the years. You also may not recall when or how your symptoms started, however it is often from a squatted position. Pain and minimal swelling are often the only signs you will experience, which last indefinitely. You may also have some knee grinding or catching, depending on the extent of the degeneration. Although your symptoms may disappear on their own, they often carry-on or return without proper treatment. If a meniscus tear goes untreated, the situation can lead to a complete tear and long-term damage. Should You Seek Medical Attention? It is recommended that you see a physician with any continued discomfort and/or pain in your knee or if you experience any of the symptoms below:
Click HERE to Go To Our Online Store We take all major credit cards and Paypal. Product Advisors are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday. Learn More About Meniscus Injuries & TreatmentsI want to learn more about Post-Surgery Recovery I want to learn all about Types, Patterns, Shapes & Severity of Meniscus Tears I want to learn more about TShellz Wrap® Circulatory Boost I want to learn more about Ice & Heat: Which Is Better For Treatment? I want to learn more about Meniscus Treatments I want to learn more about different types of Meniscus Surgery
|
        |







